FILL_XY (A, B, C) Fills missing values with average nearest neighbor values in X and Y
|
Arguments: |
DATA |
variable to fill in X and Y |
|
|
|
MASK |
Fill only where MASK=1 |
|
|
|
N |
number of fill-passes through the data |
|
|
Result Axes: |
X |
Inherited from DATA |
|
|
Y |
Inherited from DATA |
||
|
Z |
Inherited from DATA |
||
|
T |
Inherited from DATA |
This function was contributed by Martin Schmidt.
FILL_XY(data, mask,n) is a low order 2-dimensional fill utility. Data points with missing values are filled by equal weight averaging over all valid pointsof the 8 neighbors. The procedure is repeated n-times, each step starts with the result of the previous step. FILL_XY is especially useful for smooth extrapolation.
Applications can be found when mapping coarse grid ocean data to a finer grid. This is often needed for example to generate initial fields of ocean models from climatological data sets. Interpolation may fail for grid points of the destination grid with positions between an ocean point and a land point on the coarse grid. Applying FILL_XY to extrapolate ocean values into land before the data are mapped to the fine grid helps to avoid undefined values on the destination grid.
Example: generate a field with climatological SST, at the grid of etopo5 by interpolation from the coads climatology dataset:
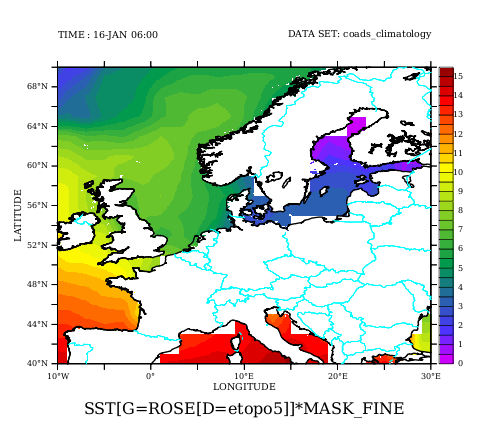
use coads_climatology use etopo5 ! Choose a region to see the effect ! (here Western Europe) set region/x=-10:30/y=40:70 ! View SST on its original grid shade/l=1/d=1 sst go land_detail thick " " light_blue
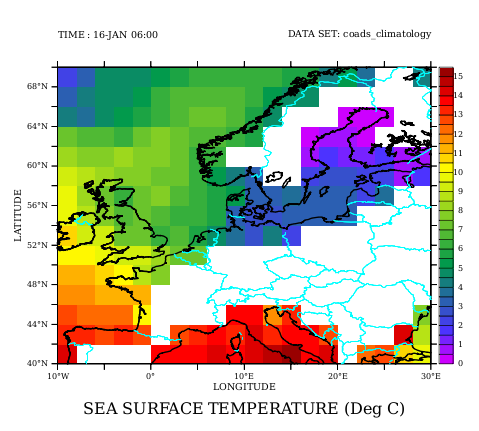
! Define a land mask for the fine destination grid let mask_fine= if rose[d=2] lt 0 then 1 else 1/0 shade/l=1/d=1 sst[g=rose[d=2]]*mask_fine go land_detail thick " " light_blue ! Note that there remain large areas with missing ! data in the ocean, for instance in the Baltic Sea ! and the Mediterranean.
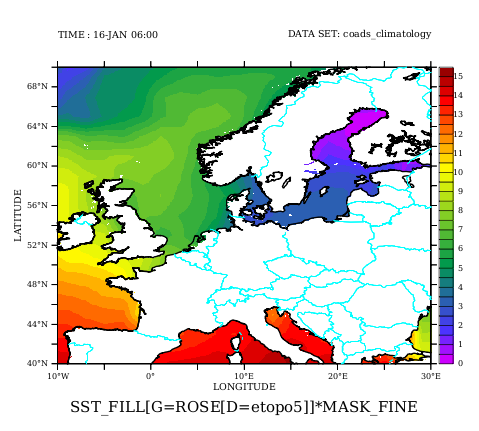
! Extrapolate the source data beyond the sea ! before regridding to the fine grid of etopo5. ! mask_fill is "1" everywhere. let mask_fill=missing(sst/sst,1) let sst_fill= fill_xy(sst,mask_fill,2) ! Now all ocean points at the fine grid are defined. shade/l=1/d=1 sst_fill[g=rose[d=2]]*mask_fine go land_detail thick " " light_blue