FAQ
Least Squares Regression
Least Squares Regression
Question:
How can I compute a regression line?
The script regresst.jnl defines variables "SLOPE", "INTERCEP", "RSQUARE", and "QHAT" given a dependent and independent variable. If you have a variable defined on the X axis, (or you can use RESHAPE to put it on an X axis) then use the script regressx.jnl
regresst.jnl offers the following coaching lines about its inputs and outputs:
... Linear Regression Along the T Axis ... Instructions: Use the LET command to define new variables Define the variable P as your independent (X) variable Define the variable Q as your dependent (Y) variable Results will be variables "SLOPE", "INTERCEP" and "RSQUARE" QHAT will be the regression estimate Note: If "T" is your independent variable then ... "SET GRID Q" after defining Q. ...
Example 1:
Define variables P and Q as the inputs to the script.
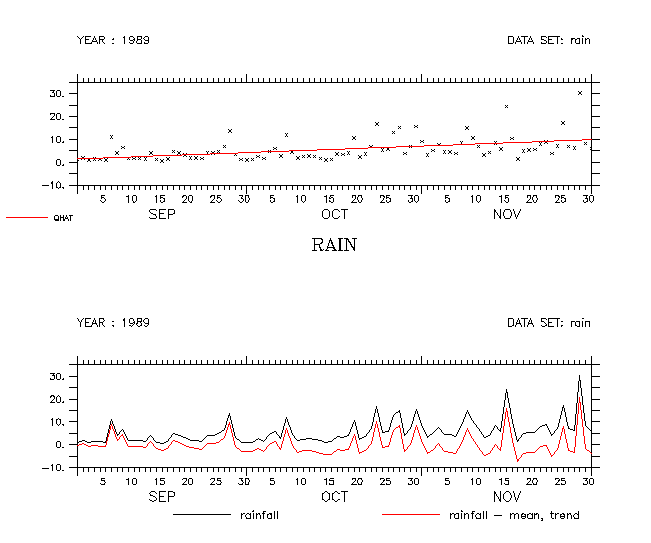
yes? USE rainfall.nc yes? LET p = t[gt=rain] yes? LET q = rain yes? SET GRID q yes? GO regresst
Here are our definitions of P and Q, and some of the variables that the script defines. One might want to use QAVE or QVAR, the mean and variance of variable Q.
yes? SHOW VAR Created by DEFINE VARIABLE: >>> Definitions that replace any file variable of same name: P = T[GT=RAIN] Q = RAIN ... PAVE = PMASKED[T=@AVE] QAVE = QMASKED[T=@AVE] PVAR = PPAVE - PAVE*PAVE QVAR = QQAVE - QAVE*QAVE SLOPE = PQVAR / PVAR INTERCEP = QAVE - SLOPE*PAVE QHAT = SLOPE*P + INTERCEP RSQUARE = (PQVAR*PQVAR) / (PVAR*QVAR)
Show the input data as a scatter point, and the regression line
yes? SET VIEW upper yes? PLOT/SYM q yes? PLOT/OVER qhat
Subtract qhat from the variable to get the series, minus its mean and trend.
yes? SET VIEW lower yes? LET/TITLE="rainfall - mean, trend" detrended = rain - qhat yes? PLOT rain, detrended
Now show the setup for regressions between two variables which are functions of T, X, Y, Z
Example 2:
Setting up the call to compute the regression between two dependent variables in T. Define variables which depend only on T.
yes? use monthly_navy_winds yes? let p = uwnd[x=90E:120W@ave,y=-90:-45@ave,T=1-jan-1985:31-dec-1990] yes? let q = vwnd[x=90E:120W@ave,y=-90:-45@ave,T=1-jan-1985:31-dec-1990] yes? set grid q yes? go regresst yes? plot/vs p,q yes? plot/over/vs/line/color=blue p,qhat
Example 3:
Setting up the call to compute the regression between two dependent variables in X. Define variables which depend only on X. Here we're comparing UWND for x=0:360 at different times. Calls to the regressy and regressz scripts would be similar, sending variables that are lines in Y or Z.
yes? use monthly_navy_winds yes? let p = uwnd[y=-90:-45@ave,T=15-jan-1985] yes? let q = uwnd[y=-90:-45@ave,T=15-jun-1985] yes? set grid q yes? go regressx yes? plot/vs p,q yes? plot/over/vs/line/color=blue p,qhat
Example 4:
This example comparing all the data on the globe at two different times. Use XSEQUENCE to put the data onto an abstract X axis
yes? use monthly_navy_winds yes? let p = XSEQUENCE(uwnd[T=15-jan-1985]) yes? let q = XSEQUENCE(uwnd[T=15-jun-1985]) yes? set grid q yes? go regressx yes? plot/vs p,q yes? plot/over/vs/line/color=blue p,qhat
